Career framework
| Site: | Royal College of Midwives |
| Course: | Career framework - open access |
| Book: | Career framework |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 27 February 2026, 9:15 PM |
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to the career framework
- 2. Education
- 3. Clinical practice
- 4. Management
- 5. Research
- 5.1. Research training and study
- 5.2. Masters researchers case studies
- 5.3. PhD researchers case studies
- 5.4. Professional doctorate
- 5.5. Clinically-based research roles
- 5.6. Clinical academic midwife
- 5.7. Portfolio-based research midwife
- 5.8. Consultant midwife
- 5.9. University-based research roles
- 5.10. Lecturer
- 5.11. Research fellow
- 5.12. Associate professor / Reader
- 5.13. Professor
- 6. Resources and links
1. Introduction to the career framework
![]() The aim of the RCM Career framework is to provide a profession specific career structure for our members, their employers and educators across the United Kingdom.
The aim of the RCM Career framework is to provide a profession specific career structure for our members, their employers and educators across the United Kingdom.
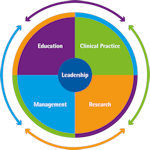
The framework is built on the four pillars of education, clinical practice, management and research. Where other frameworks have considered leadership as part of management, we have placed leadership centrally within the four pillars as we believe leadership is everyone’s responsibility and is an important part of everyone’s role.
In this first iteration of the RCM Career Framework we have focused on the three pillars of education, clinical practice and management within universities and the NHS. While the research pillar continues to be built you will see elements of research in many of the roles included in the other three pillars. Future versions will include other arenas where you may want to take your career.
Not everyone will be able to see their role or job title because roles and titles are frequently unique to people and their employers. The framework is organic and provides illustrations of a sample of destinations beyond entry to the maternity workforce. It is about expanding your horizons and prospects.
The framework will continue to evolve and develop in the coming months so please feel free to share with us how it helps you. Your experiences and case studies are also welcome. Please contact education@rcm.org.uk for further information.
2. Education
![]() Midwifery education is an attractive and rewarding career devoted to the preparation of dynamic, innovative and world class midwives who deliver safe, high-quality care to women and babies. Registered midwives might work with students in the university, in the practical placement setting or in both university and practical settings.
Midwifery education is an attractive and rewarding career devoted to the preparation of dynamic, innovative and world class midwives who deliver safe, high-quality care to women and babies. Registered midwives might work with students in the university, in the practical placement setting or in both university and practical settings.
Practice educators support students in their clinical practice learning, they are based in and normally paid by the Trust or Health Board. Lecturer practitioners work both in the university and placement setting, with their time split between each.
Midwifery lecturers are normally based in universities and they usually focus on teaching plus one of these areas: research and scholarship, leadership and management or clinical practice. The various job titles may reflect these responsibilities.
Click the next page arrow to work through each role or select the roles that interest you from the table of contents on the right.
 The following i-learn courses can support you in a move to working in education:
The following i-learn courses can support you in a move to working in education:
- A range of leadership courses - search for leadership using the search icon (magnifier) at the top of this page
- Familiarising yourself with i-learn content generally and sharing useful courses with your students
2.1. Associate lecturer, assistant lecturer or midwifery tutor
![]() Many universities have created opportunities for midwives who might be interested in starting a career in midwifery education. There are various titles for this role, such as assistant lecturer or tutor in midwifery.
Many universities have created opportunities for midwives who might be interested in starting a career in midwifery education. There are various titles for this role, such as assistant lecturer or tutor in midwifery.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click for a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case studies
Click the image hotspot below to read a case study:
Rachael Martin, teaching associate, briefly describes her role (1.43 minutes):
2.2. Lecturer practitioner
![]() Lecturer practitioners are experienced midwives and bring practice-based skills to enrich midwifery education courses. They contribute to clinical skills development and help integrate the student’s theoretical knowledge with professional practice.
Lecturer practitioners are experienced midwives and bring practice-based skills to enrich midwifery education courses. They contribute to clinical skills development and help integrate the student’s theoretical knowledge with professional practice.
Lecturer practitioners are normally based in the NHS Trust (or Health Board) but work both in the university and in the placement Trust. The time allocated to each organisation varies, for example it could be 50:50.
Click each heading for more information about the lecturer lractitioner role:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case study
Are you working in the role of lecturer practitioner? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
2.3. Lecturer
![]() This inspirational career provides excellent opportunities for experienced midwives to use their academic knowledge and clinical practice expertise, along with their leadership and management skills, to contribute to the life chances of women and babies through educating midwives.
This inspirational career provides excellent opportunities for experienced midwives to use their academic knowledge and clinical practice expertise, along with their leadership and management skills, to contribute to the life chances of women and babies through educating midwives.
Midwifery lecturers usually work in universities using a wide range of activities such as lectures, seminars, tutorials, role play and skills laboratories. They are also responsible for assessments and developing the curriculum.
Working in higher education has a number of advantages such as flexibility in working patterns, job security, a clear career progression path and a decent salary. However, the work can be challenging and complex, with many internal and external factors shaping the experience.
Click the headings for more detail:
Click to download a more detailed PDF of the role.
Case studies
Click the image hotspots to read some case studies:
2.4. Practice education facilitator
The clinical practice education facilitator (PEF) mainly supports students with their clinical practice learning in the placement trust (or health board) and the university. Like the lecturer practitioner the practice educator strengthens the links between the Trust and the university. They are experienced midwives who focus on developing students' clinical skills; this includes teaching, assessments and supporting mentors.
The PEF works in practice and with the university, to ensure the clinical placements meet the learners needs and offer support to both students and mentors. They work in accordance with the NMC Standards to Support Learning and Assessment in Practice (2008).
This role plays a vital part in preparing future midwives, enabling them to deliver high quality evidence based care to women and babies.
Practice educators are usually employed by the NHS Trust or Health Board.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case study
Are you working in the role of practice education facilitator? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
2.5. Teaching fellow
![]() A growing number of universities now have teaching fellow posts as a route for midwives to develop in their education and research roles. This is often a joint education and research appointment or education and clinical appointment.
A growing number of universities now have teaching fellow posts as a route for midwives to develop in their education and research roles. This is often a joint education and research appointment or education and clinical appointment.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click for a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case study
Click the image hotspot to read a case study:
Are you working in the role of teaching fellow? If you would like to submit a case study, please contact education@rcm.org.uk.
2.6. Senior lecturer
![]() Senior lecturers usually work in universities and deliver education using a range of activities such as lectures, seminars, tutorials, role play, practical demonstrations and simulation. They are responsible for planning and developing the curriculum and assessments.
Senior lecturers usually work in universities and deliver education using a range of activities such as lectures, seminars, tutorials, role play, practical demonstrations and simulation. They are responsible for planning and developing the curriculum and assessments.
This inspirational career provides excellent opportunities for experienced midwives to use their academic knowledge and clinical practice expertise, along with their leadership and management skills, to contribute to the life chances of women and babies through educating midwives.
Working in higher education has a number of advantages such as flexibility in working patterns, job security, a clear career progression path. However, the work can be challenging and complex, with many internal and external factors shaping the experience. The working week is usually Monday to Friday with national holidays off.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read through the case studies:
Rosalind Haddrill briefly describes her role (1 minute):
Nicky Clarke briefly describes her role (1.30 minutes):
Sima Hay briefly describes her role (2 minutes):
2.7. Lead midwife education
The lead midwife education is an experienced senior academic and practising midwife who provides strategic and professional leadership, advising and supporting colleagues on professional matters relating to midwifery education.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click for a PDF with more detail on the role.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read some case studies:
2.8. Associate professor
![]() Associate professors, like professors, must have a relevant PhD. They will have developed an international reputation and demonstrated evidence of new knowledge, innovation and understanding in their area of expertise. They will provide leadership and contribute to the development of the research and education profile of the university, ensuring that teaching and research are integrated throughout university activities. Their research and scholarly activity contributes positively to the research excellence framework. They also need to be able to manage, lead and coach other members of the teaching and research faculty. In addition to the above another key aspect of the role is to be able to liaise and network effectively in order to generate collaborative projects and disseminate research, its impact on practice and its evidence base.
Associate professors, like professors, must have a relevant PhD. They will have developed an international reputation and demonstrated evidence of new knowledge, innovation and understanding in their area of expertise. They will provide leadership and contribute to the development of the research and education profile of the university, ensuring that teaching and research are integrated throughout university activities. Their research and scholarly activity contributes positively to the research excellence framework. They also need to be able to manage, lead and coach other members of the teaching and research faculty. In addition to the above another key aspect of the role is to be able to liaise and network effectively in order to generate collaborative projects and disseminate research, its impact on practice and its evidence base.
Please see the section on professors for more details on the role of associate professor.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read the case studies.
2.9. Professor
![]() A professor is an academic of the highest rank and is often holder of a university chair which is a professorship commemorating a founder or donor of the university. Professors are experts in their fields.
A professor is an academic of the highest rank and is often holder of a university chair which is a professorship commemorating a founder or donor of the university. Professors are experts in their fields.
Click each heading for more information:
Click to download a PDF with more detail on the role.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read the case studies:
3. Clinical practice
The maternity workforce team provides care to women and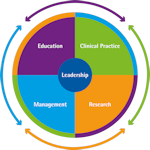 their families in all healthcare settings. That care can be in clinics in the community, hospitals and birth centres or at home during pregnancy, throughout labour and postnatally. For care delivery to make a difference for women and their families it must be competent, evidence based, high quality, safe and effective. It must be delivered with compassion and commitment to ensure good outcomes, it must also be delivered in partnership with the woman.
their families in all healthcare settings. That care can be in clinics in the community, hospitals and birth centres or at home during pregnancy, throughout labour and postnatally. For care delivery to make a difference for women and their families it must be competent, evidence based, high quality, safe and effective. It must be delivered with compassion and commitment to ensure good outcomes, it must also be delivered in partnership with the woman.
3.1. Maternity support worker
![]() A maternity support worker (MSW) is an unregistered employee providing support to a maternity team, women and their families. The MSW undertakes duties in a maternity setting, under the direction and supervision of a registered midwife or other health professional, for which midwifery training and registration are not required. MSWs support the care delivered to women and babies and their families through pregnancy, labour and the post-natal period. The title MSW is the most commonly used title to describe a support worker working in maternity but there are a range of alternative titles used that describe the same role. In Scotland the most commonly used title used is maternity care assistant (MCA).
A maternity support worker (MSW) is an unregistered employee providing support to a maternity team, women and their families. The MSW undertakes duties in a maternity setting, under the direction and supervision of a registered midwife or other health professional, for which midwifery training and registration are not required. MSWs support the care delivered to women and babies and their families through pregnancy, labour and the post-natal period. The title MSW is the most commonly used title to describe a support worker working in maternity but there are a range of alternative titles used that describe the same role. In Scotland the most commonly used title used is maternity care assistant (MCA).

MSWs can be NHS Agenda for Change pay banded at 2, 3 or 4 and the responsibilities associated with each band are covered in the following pages.
Click the link to download a copy of the RCM document: The Roles and Responsiblities of MSWs.
 The following i-learn courses can support you in furthering your career as a support worker:
The following i-learn courses can support you in furthering your career as a support worker:
- A range of courses supporting the Care Certificate. Search for Care Certificate at the top right of this page
- A range or courses on leadership
- The i-learn module Recognising the deteriorating postpartum woman is aimed at maternity support workers
- The majority of i-learn courses are relevant to support workers, use the search option to look for topics of interest, or browse through the All Courses list on the i-learn front page
3.2. Support worker band 2
![]() The maternity support worker (Band 2) is a role that delivers a range of support to the maternity team. They may also support women in their personal care and looking after their babies.
The maternity support worker (Band 2) is a role that delivers a range of support to the maternity team. They may also support women in their personal care and looking after their babies.
Maternity support workers (MSWs) may also be pay banded at 2 whilst they undertake education and training for a higher pay banded MSW post.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to download a PDF with more detail on the role.
Case study
Are you working as a maternity support worker (Band 2)? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
3.3. Support worker band 3
![]() The maternity support worker (Band 3) will undertake a range of delegated clinical duties. These may be in addition to the tasks undertaken in a Band 2 maternity support worker (MSW) role. They may work in a range of maternity settings including delivering care to women and babies in their homes in the absence of a midwife.
The maternity support worker (Band 3) will undertake a range of delegated clinical duties. These may be in addition to the tasks undertaken in a Band 2 maternity support worker (MSW) role. They may work in a range of maternity settings including delivering care to women and babies in their homes in the absence of a midwife.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click for a more detailed PDF about the role.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read case studies:
3.4. Support worker band 4
![]() The band 4 maternity support worker, in addition to the duties that a band 3 MSW could undertake, will have additional responsibilities that require higher communication and organisational skills. Examples include leading on public health initiatives such as smoking cessation, providing support to vulnerable women and their families or having responsibility for the training and development of other MSWs.
The band 4 maternity support worker, in addition to the duties that a band 3 MSW could undertake, will have additional responsibilities that require higher communication and organisational skills. Examples include leading on public health initiatives such as smoking cessation, providing support to vulnerable women and their families or having responsibility for the training and development of other MSWs.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case studies
Click on each image hotspot to read the case studies:
3.5. Midwife
![]() Being a midwife is more than just delivering babies. A midwife is usually the first and main contact for the woman during her pregnancy, throughout labour and the early postnatal period. She is responsible for providing care to the woman and baby and supporting women to make informed choices about their care.
Being a midwife is more than just delivering babies. A midwife is usually the first and main contact for the woman during her pregnancy, throughout labour and the early postnatal period. She is responsible for providing care to the woman and baby and supporting women to make informed choices about their care.
The role of the midwife is very diverse. She carries out clinical examinations, provides health and parent education and supports the woman and family throughout the childbearing process helping them adjust to their parental role. The midwife also works in partnership with other health and social care services to meet individual women’s needs, for example, teenage mothers, mothers who are socially excluded and disabled mothers.
Midwives are responsible for their own individual practice and have a statutory responsibility to keep up to date with current knowledge.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to go to the resources and links for this role.
Case study
Are you working in the role of midwife? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
3.7. Digital midwife
The digital midwife or clinical informatics midwife is an experienced midwife, with enhanced knowledge of digital issues and information technology systems within maternity. They ensure clinical practice supported by digital technology meets professional standards.
Click for a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case studies
Click image image hotspots below for some case studies:
The four core responsibilities needed to achieve this are:
Click to go to the resources and links for this role.
3.8. Labour ward coordinator
![]() The labour ward coordinator is a specialist role. They are experienced, autonomous, clinically proficient experts in the labour ward setting.
The labour ward coordinator is a specialist role. They are experienced, autonomous, clinically proficient experts in the labour ward setting.
Case study
Are you working in the role of labour ward coordinator? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
3.9. Consultant midwife
![]() The Consultant Midwife role is the highest point in the midwife's clinical career and represents clinical excellence, leadership and academic capability. Consultant midwives provide inspirational clinical leadership to ensure services for women, their babies and families reflect research and audit, are of high quality, appropriate and innovative.
The Consultant Midwife role is the highest point in the midwife's clinical career and represents clinical excellence, leadership and academic capability. Consultant midwives provide inspirational clinical leadership to ensure services for women, their babies and families reflect research and audit, are of high quality, appropriate and innovative.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case studies
Click the image hotspots to read these case studies:
Watch Michelle Knight talking about her role (1.40 minutes):
4. Management
![]() Good management in maternity care is important because it can help achieve goals, optimise resources, reduce costs, strengthen the organisation, provide stability for the workforce and improve outcomes for women. It involves the continuous management of the service, identifying and addressing challenges, implementing and evaluating solutions. This includes knowing what to do and when and ensuring that it is done in the most effective way within existing constraints.
Good management in maternity care is important because it can help achieve goals, optimise resources, reduce costs, strengthen the organisation, provide stability for the workforce and improve outcomes for women. It involves the continuous management of the service, identifying and addressing challenges, implementing and evaluating solutions. This includes knowing what to do and when and ensuring that it is done in the most effective way within existing constraints.
While there is often focus on the manager as an individual, management is also a group responsibility, particularly in the NHS or universities. Effective management helps direct efforts towards a predisposed course and involves the skill of getting things done by means of a team. It is about creating conditions that empower people to perform and operate at their best. Good managers are able to identify the right person for the job. The objectives for any management team include:
- Getting the best possible results
- Cost effectiveness
- Fairness through consistent policies
- Increasing efficiency
The RCM career framework has identified some specific management roles in the maternity workforce, although everyone has a responsibility to manage themselves and the care that provided. In this way we can ensure the delivery of high quality evidence-based care that improves outcomes for women and their families. Developing knowledge and expertise brings increasing confidence to enable you to support and manage others.
Here we illustrate some of the possible managerial roles for a midwife in the NHS.
Please go to the next pages to view the management roles.
 The following i-learn courses can support you in a move to working in education:
The following i-learn courses can support you in a move to working in education:
- A range of leadership courses - search for leadership using the search icon (magnifier) at the top of this page
- Managing change for midwifery managers
- Appraisal skills for midwifery managers
Developing personal effectiveness workshop (face-to-face training: see RCM website events page for more information and dates)
Click the link for further resources and links associated with management roles.
4.1. Senior or lead midwife
![]() The clinical midwife manager or senior/lead midwife is an experienced midwife with a hybrid role of operational management and clinical leadership and responsibility for a defined clinical area. As experienced managers they have a visible clinical and authoritative presence and will support management across the maternity setting but have professional and managerial responsibility for a defined area. At times they may be required to deputise for more senior roles within the trust/health board.
The clinical midwife manager or senior/lead midwife is an experienced midwife with a hybrid role of operational management and clinical leadership and responsibility for a defined clinical area. As experienced managers they have a visible clinical and authoritative presence and will support management across the maternity setting but have professional and managerial responsibility for a defined area. At times they may be required to deputise for more senior roles within the trust/health board.
Click each heading for more information about this role:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case study
Are you working in the role of senior or lead midwife? Please contact us about doing a case study on your career path for this page: education@rcm.org.uk
4.2. Head of midwifery
![]() A head of midwifery (HoM) within the maternity setting is a highly experienced senior midwife, manager and professional leader with an operational overview and responsibility for maternity services from acute to community provision.
A head of midwifery (HoM) within the maternity setting is a highly experienced senior midwife, manager and professional leader with an operational overview and responsibility for maternity services from acute to community provision.
They have a responsibility to support the strategic corporate leadership of maternity services and so work closely, collaboratively and productively with the Senior Midwifery team, consultant midwife, director of midwifery (DoM), the clinical director and chief nurse in influencing and providing safe, high quality clinical care, education and research across the trust or health board and community.
Click the headings for more information:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case studies
Click the image hotspot to read the case study:
Click the link for resources and links associated with the role of head of midwifery.
4.3. Director of midwifery
![]() A director of midwifery (DoM) is the most senior midwife in an NHS Trust or Health Board. The DoM provides the corporate, strategic, professional lead for delivery of maternity services. They link the strategic and operational objectives to ensure delivery of high quality and safe maternity services.
A director of midwifery (DoM) is the most senior midwife in an NHS Trust or Health Board. The DoM provides the corporate, strategic, professional lead for delivery of maternity services. They link the strategic and operational objectives to ensure delivery of high quality and safe maternity services.
Directors of midwifery have three broad roles:
- Professional leader for midwives and midwifery
- Advocate for safe, high quality maternity care, in partnership with all maternity care providers and educationalists
- Lead and manage the strategic and operational delivery of maternity services
Click on the headings below for more information:
Click to download a PDF with a more detailed role description.
Case study
Click the image hotspots to read the case studies:
Click to go to the resources and links for this role.
5. Research
![]() Midwifery research provides evidence for midwives and other healthcare professionals to use in their practice. Midwifery research will often have a clinical focus, but evidence is also required within other areas of midwifery practice, such as education, and so midwifery research can take place outside of the clinical environment.
Midwifery research provides evidence for midwives and other healthcare professionals to use in their practice. Midwifery research will often have a clinical focus, but evidence is also required within other areas of midwifery practice, such as education, and so midwifery research can take place outside of the clinical environment.
Midwives can be involved in research in many different ways. This can include being a participant in a study, undertaking a Masters or PhD level project as a post-graduate student, or going on to be employed as a researcher, often within a university or Trust/Health Board setting. A midwifery researcher may work entirely within research, in a combined education and research role, or may work in a Clinical-Academic position.
This section of the Career Framework aims to explain the opportunities available for a research career as a midwife, and to provide useful information and resources to help to support you in a move to working in research. Click the next page arrow to access the information that interests you from the table of contents on the right.
Are you working in research? If so, please get in touch so that we can feature your professional journey in a Career Framework case study: research@rcm.org.uk
5.1. Research training and study
Click each heading for information about the following types of research degree.
For information on courses and opportunities, you can browse university websites.
For information on funding opportunities, please visit the RCM website's Research hub, where you will also find information on Research support including The RCM Research Award Buddy Scheme [RABS].
Case studies
The case studies featured in this following pages will give you some examples of midwives who are currently studying at Masters, Doctoral and Post-Doctorate levels or who have completed studies.
5.2. Masters researchers case studies
Masters degrees can be taught programmes of study (MA or MSc) or research-based programmes ![]() (MRes or MPhil). In a MA or MSc programme you will typically complete an independent piece of research as your dissertation in addition to completing your taught modules, while in a MRes or MPhil programme your course will be focusing on one or more extended projects and may not contain any formal teaching. Depending on your chosen course and your preferences a Masters course can vary from between 1-3 years.
(MRes or MPhil). In a MA or MSc programme you will typically complete an independent piece of research as your dissertation in addition to completing your taught modules, while in a MRes or MPhil programme your course will be focusing on one or more extended projects and may not contain any formal teaching. Depending on your chosen course and your preferences a Masters course can vary from between 1-3 years.
Click the image hotspots to read these midwives' stories.
5.3. PhD researchers case studies
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is a purely research based degree, and the requirement of a doctoral d![]() egree is that you have generated a significant contribution to knowledge in your field of study. You do not need to have completed a Masters before commencing a PhD. PhD studies can last from between 3-4 years full time, or 5-6 years part time.
egree is that you have generated a significant contribution to knowledge in your field of study. You do not need to have completed a Masters before commencing a PhD. PhD studies can last from between 3-4 years full time, or 5-6 years part time.
Click the image hotspots to read the career journeys.
5.4. Professional doctorate
![]() These degrees are designed for professionals. A Professional Doctorate is equivalent to a PhD and will have a focus on the student’s specific professional context. Most Professional Doctorates require students to complete taught modules, all will require completion of an original piece of research. Professional Doctorate studies can last from between 3-4 years full time or up to 8 years part time.
These degrees are designed for professionals. A Professional Doctorate is equivalent to a PhD and will have a focus on the student’s specific professional context. Most Professional Doctorates require students to complete taught modules, all will require completion of an original piece of research. Professional Doctorate studies can last from between 3-4 years full time or up to 8 years part time.
Click the image hotspot to read about a midwife who it currently working towards her clinical doctorate.
5.6. Clinical academic midwife
5.7. Portfolio-based research midwife
![]() Research midwives are involved in identifying, recruiting and following up patients along with data management and support for the organisation of the clinical trials that are taking place within their organisation. They work as integrated members of a research team.
Research midwives are involved in identifying, recruiting and following up patients along with data management and support for the organisation of the clinical trials that are taking place within their organisation. They work as integrated members of a research team.
Click the image hotspots to explore the career journeys of some portfolio-based research midwives
5.12. Associate professor / Reader
![]() Associate professors will have developed an international reputation and demonstrated evidence of new knowledge, innovation and understanding in their area of expertise. They will provide leadership and contribute to the development of the research and education profile of the university, ensuring that teaching and research are integrated throughout university activities. Their research and scholarly activity contributes to the research excellence framework. They also manage, lead and coach other members of the teaching and research faculty. In addition to the above another key aspect of the role is to liaise and network effectively in order to generate collaborative projects and disseminate research, its impact on practice and its evidence base.
Associate professors will have developed an international reputation and demonstrated evidence of new knowledge, innovation and understanding in their area of expertise. They will provide leadership and contribute to the development of the research and education profile of the university, ensuring that teaching and research are integrated throughout university activities. Their research and scholarly activity contributes to the research excellence framework. They also manage, lead and coach other members of the teaching and research faculty. In addition to the above another key aspect of the role is to liaise and network effectively in order to generate collaborative projects and disseminate research, its impact on practice and its evidence base.
Click the image hotspots to read their case studies.
5.13. Professor
![]() A professor is someone who has been promoted to the highest academic grade in a university. This will usually be on the basis of their scholarly achievements. Each university will have their own policy about promotion to a professorship.
A professor is someone who has been promoted to the highest academic grade in a university. This will usually be on the basis of their scholarly achievements. Each university will have their own policy about promotion to a professorship.
Click the image hotspot to read the case study.
6. Resources and links
Click to go to the resources and links for roles listed in the career framework.